Reinforcement learning, a method of machine learning, makes use of the agent's interactions and its environment over an infinite number of time steps. A reinforcement-learning agent enters a situation st S, chooses an action at A(st) and receives a reward rt + 1 5R. This time step ends and the agent is in a different situation st+1 S.
Machine learning
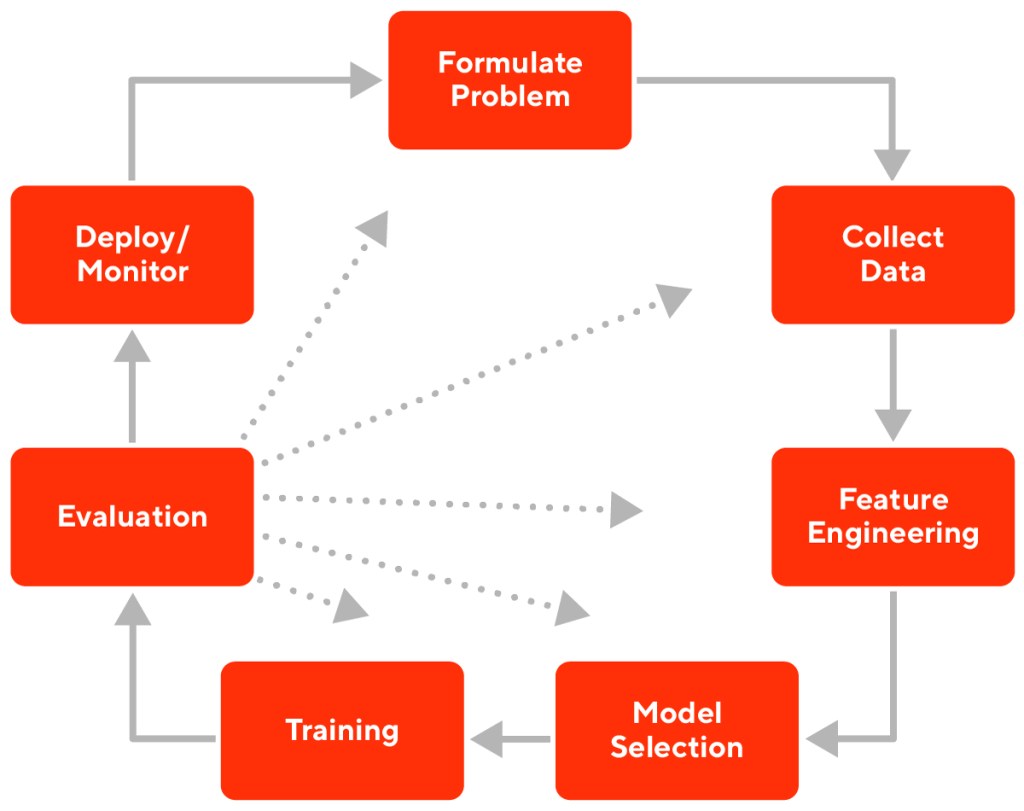
Applying machine learning to reinforcement-learning presents many challenges. The task being performed by the agent will dictate the training environment. For example, a simple game or chess could be trained in an easy environment. But, an autonomous vehicle requires a fully-realistic simulator. In this article we will examine some of these key issues when implementing machine learning for reinforcement in real-world applications.
Dopaminergic neurons
A central role in reinforcement learning is played by dopaminergic neurons. For researchers to understand how these neurons function, they must be able to comprehend both the neurophysiological wiring and the algorithms. Pavlov's famous experiment, in which a dog salivated after hearing a sound, is an excellent example of this process. This is an example of conditioned reaction, which is one of the most fundamental empirical regularities in learning.
Architectures with actor-critic components
The Actor-Critic architectures for the reinforcement learning task are based on the assumption that an action is more likely to succeed if a particular state is present. However, this assumption is not always satisfied, leading to a high variance in training. To prevent this, it is essential to have a baseline. The critic (V), then, is trained so that he or she can be as close to G. The expected return of the critic, which is non-linear, will increase the likelihood that an action is taken.
Q-value
The Q-value of reinforcement learning is a function which represents the value a particular state, or action. For example, a package's Q-value when it is picked up will likely be higher than its value going north. It is more likely that its value for going south will be lower than for going north. This value is called "value function", which represents the goodness or efficiency of the state/action. A single state may have multiple Q-values depending on its context.
Algorithms that are value-based
Research has shown that reinforcement learning using value-based algorithms produces better results than traditional methods. These methods can solve the cartpole environment with fewer sample and are therefore more reliable. But the benefits of value-based algorithms are not yet fully understood. Here are some examples. They produce better results and are more efficient. But, they can also be misleading. You should be aware of two things.
Algorithms based on policy
Reinforcement learning algorithms use a reward function that assigns values to different environments. These state-based rewards are given to agents based on the actions they take. The policy of a system determines which states, actions, and countries should be rewarded. The policy can be immediately or delayed. It describes the behaviour of the agents and what actions should earn them the most rewards. This model is then used to solve the problem of reinforcement learning.
FAQ
What can you do with AI?
There are two main uses for AI:
* Prediction – AI systems can make predictions about future events. AI can help a self-driving automobile identify traffic lights so it can stop at the red ones.
* Decision making. AI systems can make important decisions for us. Your phone can recognise faces and suggest friends to call.
What does AI mean for the workplace?
It will change our work habits. It will allow us to automate repetitive tasks and allow employees to concentrate on higher-value activities.
It will improve customer service and help businesses deliver better products and services.
It will enable us to forecast future trends and identify opportunities.
It will enable organizations to have a competitive advantage over other companies.
Companies that fail AI adoption will be left behind.
AI is used for what?
Artificial intelligence is an area of computer science that deals with the simulation of intelligent behavior for practical applications such as robotics, natural language processing, game playing, etc.
AI can also be referred to by the term machine learning. This is the study of how machines learn and operate without being explicitly programmed.
There are two main reasons why AI is used:
-
To make our lives easier.
-
To do things better than we could ever do ourselves.
Self-driving vehicles are a great example. AI can do the driving for you. We no longer need to hire someone to drive us around.
How does AI work
You need to be familiar with basic computing principles in order to understand the workings of AI.
Computers save information in memory. Computers interpret coded programs to process information. The code tells the computer what it should do next.
An algorithm is a set of instructions that tell the computer how to perform a specific task. These algorithms are typically written in code.
An algorithm could be described as a recipe. A recipe might contain ingredients and steps. Each step can be considered a separate instruction. For example, one instruction might read "add water into the pot" while another may read "heat pot until boiling."
What does AI mean today?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an umbrella term for machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, autonomous agents, neural networks, expert systems, etc. It is also known as smart devices.
Alan Turing created the first computer program in 1950. He was fascinated by computers being able to think. He proposed an artificial intelligence test in his paper, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence." The test asks whether a computer program is capable of having a conversation between a human and a computer.
John McCarthy in 1956 introduced artificial intelligence. He coined "artificial Intelligence", the term he used to describe it.
Today we have many different types of AI-based technologies. Some are very simple and easy to use. Others are more complex. They can be voice recognition software or self-driving car.
There are two major types of AI: statistical and rule-based. Rule-based AI uses logic to make decisions. For example, a bank account balance would be calculated using rules like If there is $10 or more, withdraw $5; otherwise, deposit $1. Statistics is the use of statistics to make decisions. To predict what might happen next, a weather forecast might examine historical data.
Are there any potential risks with AI?
Yes. There always will be. Some experts believe that AI poses significant threats to society as a whole. Others believe that AI is beneficial and necessary for improving the quality of life.
AI's misuse potential is the greatest concern. The potential for AI to become too powerful could result in dangerous outcomes. This includes robot overlords and autonomous weapons.
AI could also take over jobs. Many fear that robots could replace the workforce. However, others believe that artificial Intelligence could help workers focus on other aspects.
For example, some economists predict that automation may increase productivity while decreasing unemployment.
Statistics
- That's as many of us that have been in that AI space would say, it's about 70 or 80 percent of the work. (finra.org)
- A 2021 Pew Research survey revealed that 37 percent of respondents who are more concerned than excited about AI had concerns including job loss, privacy, and AI's potential to “surpass human skills.” (builtin.com)
- More than 70 percent of users claim they book trips on their phones, review travel tips, and research local landmarks and restaurants. (builtin.com)
- In the first half of 2017, the company discovered and banned 300,000 terrorist-linked accounts, 95 percent of which were found by non-human, artificially intelligent machines. (builtin.com)
- By using BrainBox AI, commercial buildings can reduce total energy costs by 25% and improves occupant comfort by 60%. (analyticsinsight.net)
External Links
How To
How to set up Google Home
Google Home is a digital assistant powered artificial intelligence. It uses natural language processing and sophisticated algorithms to answer your questions. Google Assistant allows you to do everything, from searching the internet to setting timers to creating reminders. These reminders will then be sent directly to your smartphone.
Google Home can be integrated seamlessly with Android phones. An iPhone or iPad can be connected to a Google Home via WiFi. This allows you to access features like Apple Pay and Siri Shortcuts. Third-party apps can also be used with Google Home.
Google Home, like all Google products, comes with many useful features. Google Home can remember your routines so it can follow them. When you wake up, it doesn't need you to tell it how you turn on your lights, adjust temperature, or stream music. Instead, just say "Hey Google", to tell it what task you'd like.
To set up Google Home, follow these steps:
-
Turn on Google Home.
-
Hold the Action button in your Google Home.
-
The Setup Wizard appears.
-
Click Continue
-
Enter your email address and password.
-
Select Sign In
-
Google Home is now online